Table of Contents
Introduction
Over the years, the Center for Disease Control has been working closely with different partners to ensure that long term treatments are found for many viral diseases that have continued to cause deaths and suffering to millions of people across the world. Therefore, the development of antiviral antibodies is significant in addressing the dire need for a comprehensive treatment process. With global warming and other changing conditions, viral diseases have become more common in the modern society. On the other hand, the eating patterns by people have weakened their body mechanisms to fight against viruses. For the body to respond optimally towards viral attack, it requires CD4+T cell help. Many of the experts believe that T cells depict higher levels of functional maturity when compared to the rest of the cells especially during the early ages.
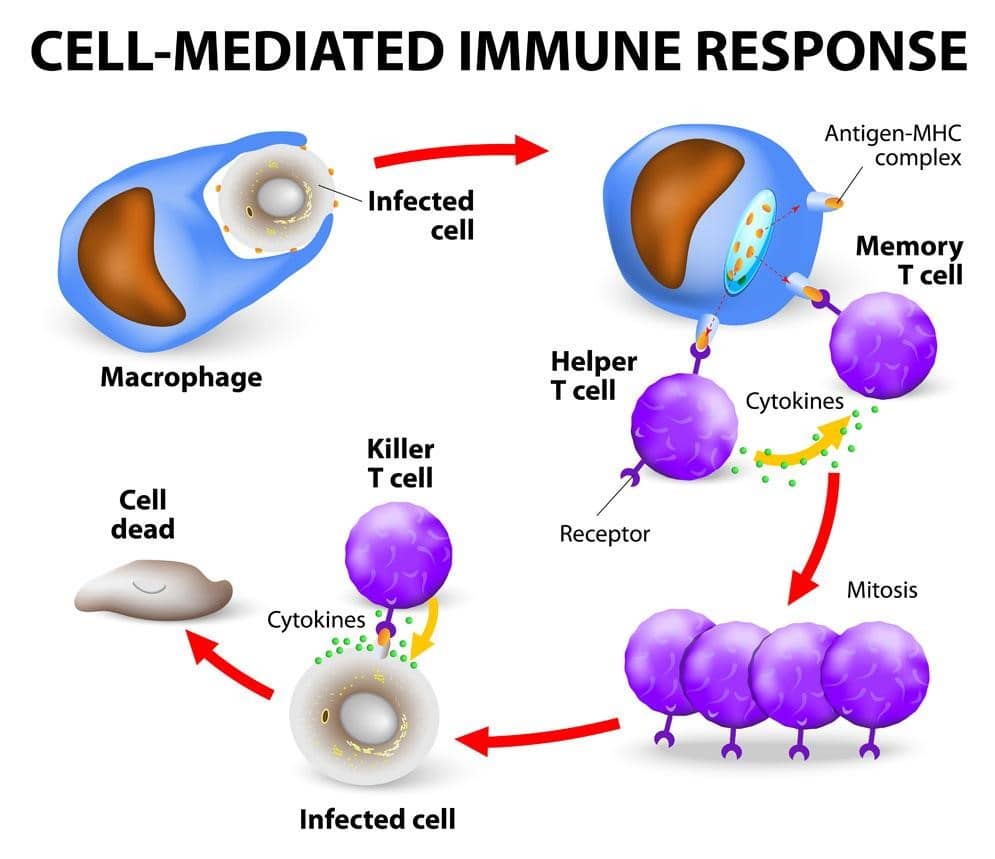
Many studies have suggested that TH2-dominant phenotype is the common neonatal response among people. Other studies on the same topic have made suggestions that TH1-type cytokines is the one that reduces the magnitude of responses. These are some of the studies that have tried to come up with a clear understanding of the functionality of human body. This is significant in developing antiviral antibodies that are well adapted to the environment. Currently, there is an increasing promise of developing antivirus antibodies that can be used to boost human body and shield it from the damage caused by viruses. Currently, mAbs forms the main category of biotherapeutics. Nevertheless, little attention has been given on the possibility of using them to treat viral infections. This is unlike in cancer and other related diseases where it has been widely used. This is a paradox especially putting into consideration that the first commercially-produced mAbs was an anti-respiratory Syncytial virus (RSV) antibody (Neuman de Vegvar, & Robinson, 2004). It was mainly used to treat respiratory-related diseases. Nevertheless, the situation is changing significantly. In the past few years, more viruses have been discovered. For instance, Ebola virus, Marburg virus, Henda virus, West Nile virus and others have become a threat to human population. There has been frequent testing of some of these mAbs with an improved second generation showing signs of neutralizing the activities of the virus. The tests have demonstrated partial efficiency when used in human bodies. In an example HIV, Ebola and HCV tests have given promise for development of high-added-value therapeutic treatment.
Role of Antiviral Antibody in Infection Control
Antiviral B cells play a significant role in defending the body against viral infections. Many of these functions are conducted by specific Ab isotypes. Some antiviral Abs role is to protect the body through neutralizing nirions through blocking viral particles at the surfaces of the cell. This prevents their fusion with the host cells. Other types of Abs are significant in agglutinating virions. They are also significant in directing lysis of virion through cascade suport. Through the support of Fc receptors in the macrophages, antiviral antibodies opsonize the viruses and infected cells (Neuman de Vegvar, & Robinson, 2004). This enhances the inclusion of viral antigens.
The responses of the body to various viral attacks can differ significantly in tier based on a specific isotope. As a result, it is important to come up with more technologies to enhance the antiviral antibodies that are directed towards a specific epitope. The reason is that different structural requirements for bidding should be taken into consideration when developing interventions that will boost the ability of the body to fight viral infections. Furthermore, detection of the antibodies can go a long way in enhancing and facilitating diagnoses, treatment, and understanding of the virus-related diseases. Currently, viral infections continue to be a major health threat across the world. Most of the antiviral vaccines that have been produced and introduced are empirically developed. There have been several cases where the viral vaccines have yielded some significant benefits. For instance, Polio, measles, mumps, and rubella are some of the diseases that have been controlled successfully from these empirically vaccines that have been developed. Currently, there is a growing list of viral pathogens with no developed vaccines. With the current advancement in technological levels, there are numerous platforms that could be used to develop vaccines to help in fighting the emerging threats from viral pathogens. Scientists have a lot of information regarding cells that are involved in antibody production. However, there is less content on the cells that are result to the storage functions i.e. memory B cells. Understanding these cells is significant in designing, developing, testing effective vaccines.

Development of Antiviral Antibody
According to a research conducted at Emory Vaccine Center and Stanford’s Department of Pathology, there is need for more effort to discover more vaccines that can be used to treat the emerging diseases such as Ebola. The research centers have been in the forefront in trying to prove that if memory B cells are activated after vaccination and infection can be used to fight other recurring viruses. Many of the countries that are suffering from Ebola and other related diseases have a history of similar infections. Therefore, majority of them had family members or their ancestors who suffered from similar ailments. As a result, the research suggests that the activation of memory B cells can have a significant role in fighting numerous diseases that are affecting the world population (Méndez-Lagares, Lu, Chen, Terrault, Segal, Khalili… Hartigan-O’Connor, 2017). According to a lead research Ali Ellbedy, those infected with Ebola are faced with a new infection. This can pose a great challenge because the body has not been accustomed to these disease-causing agents. In many cases, human body relies heavily on recall. Therefore, during vaccination and infection, the body reacts based on the past experiences. This explains the reason why the emerging viral diseases are eliminating a large number of people before the health bodies come with a way of suppressing the viruses. In the past five decades, the international bodies such as World Health Organization have been in the forefront in developing vaccines that are compatible with the current generation. The reason is that with the changing diets by the people coupled with the dynamic environment; the immune system is being attacked by numerous external agents, thereby, changing its structure.
Cells
The study showed that there is need for the development of new vaccines that will boost the memory of the body and link it with the previous infections. Researchers believe that many of the people residing in areas that experience frequent disease outbreak can be able to recover when a similar or a different disease attack their body. They argue that scientists should focus on developing a vaccine that is able to stimulate the body to produce antiviral antibody that is able to boost the immune system of the body. The study can be applied in the treatment of influenza. The reason is that influenza virus infection is the most common in the society. Although it has been ignored because many people are able to recover after the body produces enough antibodies, scientists state that influenza open channels for severe illnesses and death. This is through weakening the body immune system, thereby, exposing it to more severe diseases. Statistics indicate that there are approximately three to five million people that end up suffering from severe illnesses after suffering from Influenza. Approximately 250,000-500,000 people end up succumbing to these illnesses (Méndez-Lagares, Lu, Chen, Terrault, Segal, Khalili… Hartigan-O’Connor, 2017). Therefore, although the common strain of influenza is of public concern, there are high chances that more lethal influenza strains will emerge, an aspect that will result to pandemic cases. The recent emergence of H5N1 and H7N9 is an indication that there should be a different approach in regards to vaccine development. Human body has been found to have enough antibodies to overcome numerous viral infections. However, this requires a comprehensive approach to ensure that the intervention does not end up exposing the body to more diseases.
Researchers are looking at understanding adenoviruses in an attempt to develop improved vaccines. Andenoviruses can be described as non-developed DNA viruses that basically result to respiratory and gastrointestinal diseases. This is a major problem in young patients. The number of children across the world who have succumbed to these diseases has increased tremendously. The reason is that their parents are unable to take the necessary measures before the situation gets out of hand. Therefore, this study tried to establish whether understanding the functionality of these viruses can play a significant role in developing strains of viruses that can boost the human immune system. It relied upon young respondents who have been infected with the disease. This was significant in testing the resilience of the immune system and understanding the stages that the disease undergoes before suppressing the body. In many cases, researchers focus their attention on developing recombinant adenovirus vectors. They are widely developed for the purposes of gene and oncolytic therapies. In these cases, macrophages play an important role in detecting adenovirus and orchestrating the first response by the host response. Therefore, internalizing the adenovirus is an important step towards the improvement of the innate immune system. This suggests that the intracellular innate immune system basically responds after host’s recognition and response towards any foreign agent. This is a breakthrough in an attempt to develop more advanced vaccine that will cope with the changing immune system. There has been a major concern from the scientists that continuous use of different strains of virus will weaken the ability of the patients’ bodies to fight diseases. The diagnoses of the viruses are based on the ability to detect antiviral antibodies in human body coupled with the diagnosing of pancreatitis. In 1905, mumps were believed as the major cause of acute pancreatitis. However, since the mass production of vaccination that targeted the whole population especially after child birth, cases of mumps have decreased significantly. Therefore, scientists are looking to manipulate the existing vaccines and add some components that will fight general viral agents that might be threatening the immune systems by humans. Several studies have established that there are pathologic changes in human pancreas for those who are suffering from HIV. Therefore, the study tried to link these changes the suppression of human immune system after the attack by the virus. This information can be used extensively to develop virus that can remain effective even after the virus changes its state with the aim of becoming more resistant.
Currently, the World Health Organization in collaboration with other government and non-governmental organizations has invested heavily in research with an attempt to establish the best mechanism of dealing with the existing viral diseases and those that are emerging especially in developing countries. These bodies have linked the close interaction with wild animals as the major causes of the new outbreaks especially in Africa and South America. This study associates the change in immune system after coming together with a new strain of virus. The body overproduces or underestimates the impact of the new agents in the body, thereby, producing fewer antibodies. As a result, there is a need to understand these aspects rather than focus on producing vaccinations or developing a treatment plan before a thorough understanding of the functionality of the human body. More studies should shift their attention on the existing viral diseases that do not have treatment and continue to threaten the lives of millions of people across the world.
Microarray profiling of antiviral antibodies has given promise to the scientists that there are chances of developing diagnostics, vaccines, and therapeutic ways of treating deadly viral diseases that are posing a great health problem to people across the world. The PEPSCAN technique has been labeled as the best approach for epitope mapping to date. Over the years, researchers have been trying to improve it with the aim of reaching a large number of people and understanding the changes that happen in the body after an attack by the infectious agents. The technique identifies distinct peptides and synthesizes them through the Boc or Fmoc operation. This is done on the rods. To conduct scanning, the protein sequence is identified, an aspect that makes it possible to synthesize a series of residue peptides. Researchers suggest that residues can be introduced, thereby, creating room for the generation of mixed and more complex substitutes. For every experiment, the scientists block the sets of 96 pins. This is done against any nonspecific binding, thereby, giving room for incubation in a bowl with diluted serum. This technique was initially used to define the epitope of the coat protein. Since then, it has been used in developing numerous research papers, an aspect that indicates that it has revolutionized the medical sector in the world. Nevertheless, although it has been a success in the medial sector, it has several drawbacks. The study identifies that all the tests must be done in a sequential manner. Furthermore, each pin sets cannot be reused in a day. Instead, it can only be used once before it is regenerated to the next sample. Moreover, the removal of Antiviral antibodies and degrading peptide might result to high loss of reactivity.
SPOT synthesis is another technique that is used to generate peptide arrays (Pelegrin, Naranjo-Gomez & Piechaczyk, 2015). Unlike the previous technique, it has expanded exponentially beyond the common aspect of mapping of linear epitope. Recently, there has been an addition of the lighting systems in the whole process. This results to microarrays that have 1300-2700 features. These arrays have a high potential for being produced in large quantities. Nevertheless, they have a major limit because the length of the peptide is limited, thereby making it hard to control the level of purity. Over the years, it has become possible for the scientists to develop polypeptides using biotechniques. The methods give hope that the world is getting closer to a long-term solution to the problems that have been affecting the population for a very long-period of time.
Popular Antibody Development Studies
One of the popular antibody development studies involved a solid phase arrays. It tried to spot the arrays with different features with the aim of expanding the peptides, thereby, including the proteins, DNA, and crude extracts. The spotting technique used ink jets and printing pins to achieve its objective. The first attempts to develop antiviral antibodies were conducted by developing chips that encompassed the whole viral proteome. The study incorporated the internal calibration in cytomegalovirus and herpes simplex virus. The results indicated that there were some slight variations between slides. Moreover, there was strong correlation with the linear dose response. The study obtained similar results after using HIV and SIV proteins (Pelegrin, Naranjo-Gomez & Piechaczyk, 2015). The popularity of this study is based on the aspect that it can be used in mass production of the virus. However, for this aspect to be actualized there is a need to have a strong correlation between different parties in the health sector.
Besides the technologies that have been used in this study, there are other emerging technologies that use techniques that are customized to individual markets. The technologies make it possible to couple the antiviral antibodies to addressable tags. This happens without drying and binding the solid support. Failure to take the step into consideration would result to the interference with certain epitopes. However, one of the main disadvantages of these technologies is that antiviral antibodies produced must be mixed together with a tag that is addressable. Generally, the antiviral antibodies that are produced during the initial immune response vary based on the person infected, the route of entry and infection, and the microbes that have attacked the body. Therefore, understanding the specificities of the antiviral antibodies is significant in developing vaccines that are specific to certain individuals. Over the years, many of the vaccine manufacture produce in masses without targeting a particular population. However, the reaction towards the vaccine differs significantly from one person to the other. For instance, Hepatitis B is an ideal example of how antiviral antibodies specificity can depict the disease status of the person. The antibodies against viral envelope can be found in patients that are suffering from acute diseases. On the other hand, patients that are suffering from chronic infections lack such antibodies. Patients suffering from acute disease also respond strongly by using virus-specific T cells. This indicates the need to understand the specificity of the virus and the reaction of the body towards it. As a result, the vaccine would be in a better position to boost the immune system and enabling the body to produce antibody that are specific to the infections. The study reveals that some of the vaccines might have failed to achieve the intended purpose because they are general rather than specific to a particular agent.
According to the study, the administration of a vaccine should be preceded by proper diagnostics. There are numerous methods that are used to detect viral infections. Some of these include viral cultural, serology, and antiviral antibody tests. The viral culture is slow, thereby, requiring specific conditions according to the infection agent. Therefore, it has been labeled as ineffective especially when a quick response is required to avoid more deaths. Antiviral antibodies tests use blood samples to test the presence of these disease fighting agents. The main purpose of the vaccines is to induce immunological memory with the aim of accelerating cell-mediated responses to fight the pathogen.
Studies regarding the immune system can provide direction towards the development of vaccines. The diversity of antigenics is in existence in different viruses such as hepatitis. An ideal vaccine is the one that would elicit responses that are capable of neutralizing different spectrum of variants (Pelegrin, Naranjo-Gomez & Piechaczyk, 2015). This can be achieved by developing vaccines that target specific epitopes. Furthermore, developing vaccines that can target various epitopes can save resources and achieve better results. A patient that is able to react against epitopes that of interest to vaccination production were used in the studies. The results obtained indicate that it’s critical to target the specific T cells to boost their level of responses. The approach can be used to produce vaccines such as those of HIV that are specific to certain strains found in some parts of the world.
The sensing of viruses is a significant component for the host. The reason is that after recognition of the viral agents, the body of the host is able to respond by producing cytokine and type 1 1fn, thereby, enabling the body to develop an adaptive immunity. In a study by Zaiss, Vilaysane, Cotter, Clark, Meijndert, Colarusso, … Muruve, (2009), the results indicated that adaptive immune system and antiviral antibodies are able to subvert the natural tropism. The researchers were able to prove that it is possible to boost the ability of the body to handle viral agents by improving the strengths of memory B cells.
Future Development
The studies can be developed further by testing hosts from different parts of the world. The reason is that results from the researches indicate that external conditions might have an impact on the host reactions towards viral infection. Therefore, to understand the body reactions, it’s significant to expose the test agents to different weather conditions and other related factors to observe whether the environment can be used to boost the chances of recovery.
Antiviral antibodies development can be developed further by investing more on the modern technologies. Over the years, the researchers have been relying on the equipment that was developed decades ago. Little attention has been directed towards developing technologies that will support further research in the medical field. Therefore, there is a need for different partners to work together in achieving this objective.
- Méndez-Lagares, G., Lu, D., Chen, C., Terrault, N., Segal, M. R., Khalili, M., … Hartigan-O’Connor, D. J. (2017). Memory T Cell Proliferation before Hepatitis C Virus Therapy Predicts Antiviral Immune Responses and Treatment Success. The Journal of Immunology, 200(3), 1124-1132.
- Neuman de Vegvar, H. E., & Robinson, W. H. (2004). Microarray profiling of antiviral antibodies for the development of diagnostics, vaccines, and therapeutics. Clinical Immunology, 111(2), 196-201.
- Pelegrin, M., Naranjo-Gomez, M., & Piechaczyk, M. (2015). Antiviral Monoclonal Antibodies: Can They Be More Than Simple Neutralizing Agents? Trends in Microbiology, 23(10), 653-665.
- Zaiss, A. K., Vilaysane, A., Cotter, M. J., Clark, S. A., Meijndert, H. C., Colarusso, P., … Muruve, D. A. (2009). Antiviral Antibodies Target Adenovirus to Phagolysosomes and Amplify the Innate Immune Response. The Journal of Immunology, 182(11), 7058-7068.

