Table of Contents
Abstract
The Six Sigma framework provides the basis upon which the development of a new product could lead to the reduction of production costs, quality improvement and the satisfaction of a firm’s customers. This framework informs the primacy of this paper, which dwells on the provision of background information on the management model. Conversely, the paper covers the methodological aspect that could be applicable to the development of a new product. For this reason, the methodology focuses on the DMAIC performance improvement model applicable to this framework. The process leads to the conclusion that the model is essential for evaluating the procedure needed for the development of a new product, which assists in the improvement of the process.
Introduction
Six Sigma could be understood as a standard used by a company to improve the performance of its business and ensure the satisfaction of its customers. Motorola developed the management strategy in the year 1986, during a period when a considerable number of manufacturing entities were seeing a revolution in their operations (Thakore, Dave, Parsana, & Solanki, 2014). This period saw numerous consumer demands arise, prompting the manufacturing companies to consider the significance of customer satisfaction to ensure their survival in the market. For this reason, the firms were forced to enhance not only the quality of their products, but the quality of their processes as well. The Six Sigma business management strategy was essential for the improvement of quality while following up on the costs of production.
In the light of the identified elements regarding Six Sigma, this paper provides an overview of the management model, consequently summarizing its distinctive elements. Conversely, the paper looks into several concerns regarding its effectiveness in an organization. The provisions recognize the idea that achieving high productivity in a company characterizes the fundamental element defining production. In spite of this essential element, it would be necessary for a company to consider other factors that fulfill various needs such as customer demands, competition, product diversity, and lead time demands, among other provisions. The benchmark of this strategy considers these elements. The primary initiative of the strategy involves reducing variations in the manufacturing process, consequently reducing production costs and processes.
Definition and background of Six Sigma
As identified earlier, Motorola invented the lean tool (Thakore, Dave, Parsana, & Solanki, 2014). The need to create this tool emanated from the organization’s desire to minimize production costs and improve the quality of its products. Just as several other companies that were operational in this period, the capability of the production processes were low, with a large portion of the producers failing to meet some of the demands from customers. The failure to meet customer requirements meant that most of their products needed rework, some of them were scrap, the business entity needed to perform field services to ensure customer satisfaction, and it had to recall some of the products already shipped to other markets outside the local market.
The rationale for coming up with this strategy emanated from the need to reduce the costs incurred during production, reduce possible wastages, and ensure that the customers were satisfied with the firm’s products and services. This need saw the birth of the Six Sigma concept, developed by Motorola engineers, which contributed to the firm’s bottom line (Thakore, Dave, Parsana, & Solanki, 2014). The application of this strategy would enable the company to achieve a “3.4 Defects per Million Opportunities (DPMO)” (Panneerselvam, 2012). Motorola’s achievement influenced other companies, such as General Electric (GE), during which it underwent a significant evolution. GE enhanced the model, consequently infusing it to every section of the business to ensure its success (General Electric, n.d). This infusion enabled GE’s business to realize an improvement in its financial performance, similarly benefiting its employees, shareholders, as well as consumers. The then CEO claimed the quality improvement model to be an integral part of the firm’s culture (General Electric, n.d).

Methodology
Using Six Sigma the procedure that would be in place for the development of a new product will be the primary concern. The fundamental strategy is to upgrade a firm’s competitiveness. The procedure will focus on meeting quality demands, the delivery time, and the cost limitations that an organization might encounter. For this reason, this development will focus on Six Sigma’s DMAIC process. In the light of this provision, the initial step in the development of the new product would involve the definition and provision of its layout. Since the development of the product will be computer-aided, it would be essential to designate given codes for the different production phases hierarchically. This section also involves the definition of control items, which are inclusive of the presentation of the schedule, the production capability and capacity, and regulatory elements, among other provisions.
The next step, which falls in the measurement domain, focuses on the use of a method that will assist in measuring the performance of the process. One of the possible methods that could be used in measuring the performance index of the product development process is the use of questionnaires. The indices considered for inclusion in the questionnaire cover the importance of the new product and its execution. The other phase attends to the performance evaluation and factor analyses. Factor analysis focuses on finding primary elements that can affect the performance of the product development procedures (Jou et al., 2010).
On the other hand, the performance evaluation analysis, which looks into the work performance standards, reveals possible work items and resources distributed unevenly. For this reason, it would be possible to focus on a strategy that will improve the production process and reduce inefficiency. During this phase, it is possible to locate some of the variable work items that fall outside the confines of the evaluation matrix.
Figure I: Reality chart providing the execution of the new product development
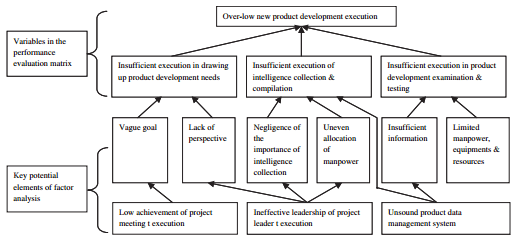
Source: Jou et al., 2010
The other phase is the development phase that focuses on the improvement of the development procedure as well as the establishment of the complete product development system. In relation to the aspect of improvement, it would be essential to realign the management skills that would assist in meeting the objective of the project, which involves the decision-making aspect of the product. When establishing the system, several provisions are fundamental. These elements are inclusive of collecting appropriate information, developing testing and examination systems, and data processing systems. The verification phase uses the system application that can process data based on the object-oriented technique used in the development phase. The process makes it possible for users to establish a plan and system that follows the different strategic and scales applicable to the product development mechanism.
Figure II: The phases of the Six Sigma Process
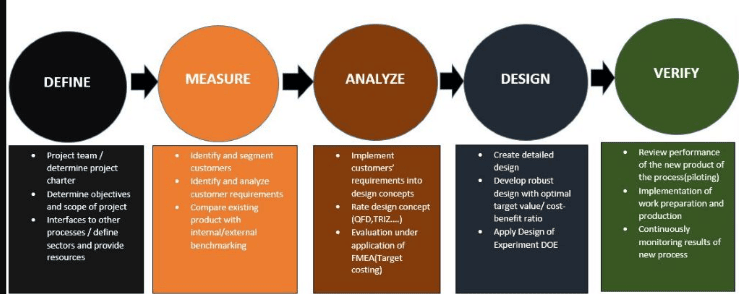
Results
The study considered several aspects that are inclusive of performance and factor analyses, among other provisions, into the Six Sigma framework. This framework works towards the improvement of the quality of the new product, consequently leading to the development of a system that would assist in the evaluation and improvement processes. A company can use the described model to evaluate the production of a new product systematically since it assists in revealing possible problems, analyzing their causes and establishing schemes that could assist in their execution and considered improvements. The systematic provisions are essential for the realization of appropriate product development procedures necessary for enhancing the producer’s competitiveness.
Discussion and conclusion
The discussed model assists in evaluating and improving the performance of procedures that can assist in the development of a new product. It does not focus on the development of a performance index applicable to the production system but the systematic steps necessary for identifying, analyzing and assisting in the improvement of procedural entities applicable to the development of a new product. The entities primarily assist in the identification of elements that might degrade performance in relation to the process of a new product development. A suggestion that would assist in further research would include the implementation of studies that could determine whether the model would be applicable in any industry. However, the adoption of the proposed model would assist in the enforcement of manufacturing provisions such as the competitiveness of the new products.
- General Electric. What is six sigma? The roadmap to customer impact. Retrieved July 28, 2016, from http://www.ge.com/sixsigma/SixSigma.pdf
- Jou, Y. T., Chen, C. H., Hwang, C. H., Lin, W. T., & Huang, S. J. (2010). A study on the improvements of new product development procedure performance-an application of design for Six Sigma in a semi-conductor equipment manufacturer. International Journal Of Production Research, 48(19), 5573-5591.
- Panneerselvam, R. (2012). Production and operations management. New Delhi: PHI Learning Privated Limited.
- Thakore, R., Dave, R., Parsana, T., & Solanki, A. (2014). A Review: Six Sigma Implementation Practice in Manufacturing Industries. Int. Journal Of Engineering Research And Applications, 4(11), 63-69.

